Quantitative analysis of experimental animals
A total of 35 rabbits were included in the final analysis, no drop out.
General morphology of bone defect region of rabbits after transplantation of bio-ceramic combined with bone marrow stromal stem cells and bone morphogenetic protein
Experimental group: At 4 weeks after model induction, bio-ceramic tightly connected to surrounding soft tissues. Soft tissues had many scar tissues, with brittle texture. Numerous soft new callus was visible surrounding and in the bio-ceramic. A small quantity of bone bridging was found. At 8 and 12 weeks, callus formation was apparently increased surrounding and in the bio-ceramic. The bio-ceramic was mostly replaced by new bones. Perfect bone bridging was visible in the transplanted region. At 24 weeks, the bio-ceramic was mostly replaced by new bones. Bone defect region was completely connected to bone end. Bone defect region could not be distinguished by naked eyes. Control group: at 4 weeks, very few calluses were seen on both ends of bio-ceramic bone area, and bio-ceramic mostly remained. At 8 and 12 weeks, less new bone formation was observed, and bio-ceramic remained. At 24 weeks, bio-ceramic was partially replaced by new bones. Bridging and moulding were poorer than in the experimental group. Blank control group: at 24 weeks after model induction, no new bones formed in each defect area. Fracture site sclerosis was observed, canal closed. The defect region was filled with a large number of fibrous connective tissue.
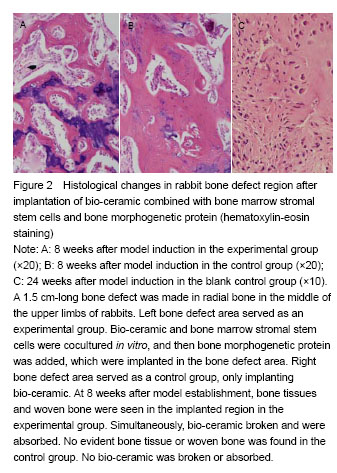
Radiograph results in the bone defect region of rabbits after transplantation with bio-ceramic combined with bone marrow stromal stem cells and bone morphogenetic protein
At 4 weeks, more callus formed in the bone defect region, and partial bone bridging formed in the experimental group. Very few calluses formed in the bone graft region in the control group. The transmittancy was greater in the control group than in the experimental group at the same stage. At 8 and 12 weeks, new bone formation gradually increased in the transplanted region. Bone bridging formed and connected between both bone ends. Bone remodeling was still moderate. In the control group, very few callus formed in the transplanted region. The transmittancy was greater in the control group than in the experimental group in the same period. At 24 weeks, new bone was connected to cortical bone of broken ends. Most marrow cavity was recanalized. Moulding was complete in the bone graft region. In the control group, bone ends of the bone graft region were partially bridged, with the presence of poor moulding and the absence of recanalization of the marrow cavity. In the blank control group, at 24 weeks, no new bone tissues were visible in the bone defect region. Fracture site sclerosis was visible, and bone marrow closed (Figure 1).
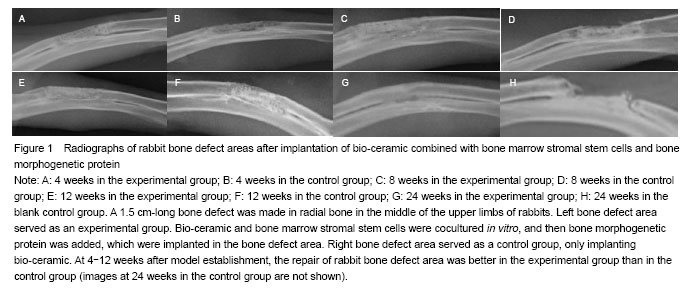 Histological changes in rabbit bone defect area after implantation of bio-ceramic combined with bone marrow stromal stem cells and bone morphogenetic protein
Histological changes in rabbit bone defect area after implantation of bio-ceramic combined with bone marrow stromal stem cells and bone morphogenetic protein
As displayed in Figure 2, in the experimental group, at 2 weeks after model establishment, many soft tissues stuck around bio-ceramic, and chondrocytes were visible. At 4 weeks, a large number of mesenchymal cells, fibroblasts and chondrocytes were observed in and on the edge of bio-ceramic carrier. Original marrow cavity formed. New capillary grew in the bio-ceramic. At 8 and 12 weeks, bone tissue, woven bone, primitive bone marrow and bone marrow cavity formation were found in the implanted area. Obvious boundary line was seen in the juncture of new bones and original bio-ceramic. Moreover, new osteocytes were found. Simultaneously, bio-ceramic carrier fragmentation and absorption were found, and the ingrowth capillary became thick (Figure 2A). At 24 weeks, mature bone trabecula were detected among broken bone and new bones. New cortical bone was detectable outside bio-ceramic. New Harvard system was visible. Bone contour units were irregular. “Trim”-like bone cells were detected near the edge of the inner canal. A large number of lamellar bone formed. Marrow cavity and lacunae apparently formed, with the presence of numerous bone marrow cells and fat drop. Original bio-ceramic broke and absorbed evidently. Blood capillary grew into nourishing blood vessels. Simultaneously, broken bone resorption and osteoblastic activity were carried out among external newly-formed cortical bone and bio-ceramic. In the control group: at 4 weeks after model induction, mesenchymal cells, fibroblasts and a few chondrocytes were visible on the edge of bio-ceramic. New blood capillary was occasionally found in bio-ceramic. At 8 and 12 weeks, many chondrocytes were visible. However, obvious bone tissue and woven bone were not seen. No bio-ceramic broke or absorbed. Blood capillary was occasionally found (Figure 2B). At 24 weeks, bone tissue and woven bone were observed. Primitive bone marrow and marrow cavity formed. Original bio-ceramic broke and absorbed. Blood capillary grew into nourishing blood vessels. Bonding wire of new bones and bio-ceramic was evident. In the blank control group: at 24 weeks after model establishment, a large number of fibrous connective tissue formed in the bone defect region (Figure 2C).
Biocompatibility and adverse reactions after implantation
After model induction, activities in rabbits were normal. Diet, stool and urine were normal. No wound redness, oozing, infection or dehiscence were seen. Wound was healed in the first stage. Bio-ceramic combined with bone marrow stromal stem cells and bone morphogenetic protein after implantation showed good biocompatibility.